Eleven versions of simple epithelia structure
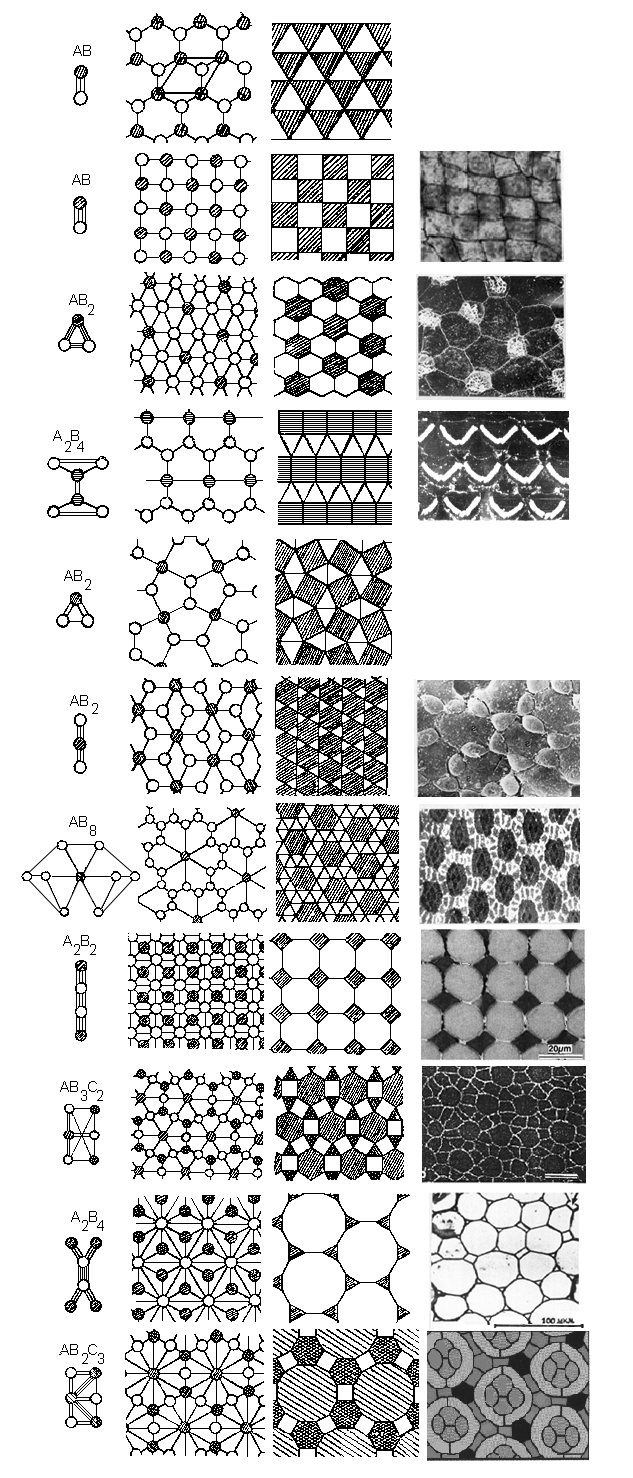
All possible variants of 2-D cell sheets spatial organisation.
Here and further the elementary morphofunctional tissue units (ETU) are
presented in the left part of the Fig. and their cell composition is noted,
the schemes of tissue topology are in the middle part. The tissue
geometrical models are in the next part of the Fig. In the right part
of the Fig. are the patterns of the cell connections in the real tissues (from Savostyanov 2001a).
The mosaic examples follow from up to down:
- The mosaic of two types of cells shows a checkerboard pattern in the
luminal surface of an avian oviduct epithelium.
Modified from Honda, Yamanaka a. Egushi 1986;
- Mosaic, consisting of ciliary and villous cells in the ratio 1/2 in
the frog embryo ectoderm. Modified from Landstrom 1977;
- Mosaic, consisting of receptory (possessing stereocili) and
supporting cells (triangle) in the Corti's organ. Modified from
Engstrom a. Borg 1983;
- Mosaic, consisting of gexagonal Sertolii's -S and triangle
spermatogonia cells in the rat deferent canal.
Modified from Nagano a. Suzuki 1983;
- Mosaic, consisting of receptory and pigment cells in the developing
Drosophila eye. Modified from Fehon et al. 1991;
- Mosaic from rectangular and octagon cells in the geckos retina.
Modified from Loew, Govardovskii, Pohlich, Szel, 1996;
- Mosaic, consisting of gexagonal, rectangular and triangles cells in
the Basilar Papilla of chicken embryons.
Modified from Goodyear and Richardson 1997.
- Mosaic, consisting of triangles and twelvegonals in the parenchymal
tissue of the celery stalk. Modified from Esau 1980.
- Mosaic, consisting of ommatidia (considering as a solid element) and
interommatidial (pigment) cells in Drosophila retina. Modified from
Miller D.T., Cagan R.L. 1998.
- The blanks correspond to undiscovered tissue variants.
Back to the
Reconstruction of 3-D epithelial architecture
Back to the Picture Gallery
Back to the Homepage

